- The History of AI Regulation in the US across Administrations
- Obama Administration
- Trump Administration
- Biden Administration
- The AI Bill of Rights - Things to Take Care of during AI Development
- Effective and Safe Systems
- Algorithmic Discrimination
- Data Privacy
- Notice and Explanations
- Human Alternates
- The Executive Order - 7 Key Actions to Ensure during AI Development
- New Standards for AI Safety and Security
- Protecting Americans’ Privacy
- Advancing Civil and Equity Rights
- Standing up for Patients, Customers, and Students
- Supporting Workers
- Promoting Competition and Innovation
- Effective and Responsible Government Use of AI
- What Businesses Can Do to Prepare for AI Compliance in Software Development?
- Know the AI Model
- Set the Foundation for AI Adoption
- Design Accountability Structures
- Risk assessments
- Communicate
- FAQs
On May 16th, 2023, Sam Altman testified before Congress saying it is time for the regulators to set limits on AI systems. “If this technology goes wrong, it can go quite wrong,” he said, claiming it might do “significant harm to the world.” Sam’s views resonated with the lawmakers who felt that government involvement would be crucial when mitigating the risks.
A topic placed on low priority over a year ago, governments are now fiercely discussing the need to put AI regulation in the US, leaving businesses in a mode of uncertainty about their focus.
In August 2024, California’s proposed SB 1047, a groundbreaking but controversial bill aimed at preventing AI-driven disasters before they happen, was passed by the legislature and is now pending for final approval from the state. The bill requires AI companies in California to implement safety measures before training advanced AI models, such as ensuring the ability to shut down models quickly, protecting against unsafe modifications, and testing for potential catastrophic risks.
Thus, the increasing adoption of AI across industries, coupled with warnings given by Sam Altman, Steve Wozniak, and Elon Musk, the passing of the bill SB 1047 as well as the rising number of lawsuits against AI, Machine Learning, and Generative AI, highlights the need for stronger US AI regulations.
With a dedicated focus on the USA, let us look into the many ways the AI compliance in software development is developing, essential for businesses aiming for AI-based products for enhanced growth.
Also Read: AI Regulation and Compliance in EU: Charting the Legal Landscape for Software Development
The History of AI Regulation in the US across Administrations
Over the years, several artificial intelligence compliances have come into the picture from the end of The White House, Federal Trade Commission, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Congress, and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau. Looking at how the different administrations approached AI regulatory compliance would be the best way to understand the legal scenario.
Obama Administration
The earliest examples of federal artificial intelligence regulatory compliance were sketched by President Barack Obama’s administration, in a public report called “Preparing for the Future of Artificial Intelligence,” issued by the National Science and Technology Council in October 2016. It contained the details of AI usage in the economy and federal government at the time while talking about fairness, governance, safety, and global security.
Released a day later to the report, the National Artificial Intelligence Research and Development Strategic Plan identified the critical areas for federal-funded AI research, “with particular attention on areas that industry is unlikely to address.”
Trump Administration
Another key development occurred when President Donald Trump signed Executive Order 13859, called “Maintaining American Leadership in Artificial Intelligence,” in February 2019. The AI government regulation set the American AI initiative in action, which then led to the issuance of technical standards and guidance that would fix the scope of AI law over the following years.
The purpose of the government regulation of artificial intelligence was to inform the federal agencies’ plans to “consider ways to reduce barriers to the use of AI technologies to promote their innovative application while protecting civil liberties, privacy, American values, and United States economic and national security.”
Biden Administration
Another milestone in the USA AI laws and regulations came in October 2022 with the Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights: Making Automated Systems Work for the American People. Laid out by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy, the document contained five principles to “guide the design, use, and deployment of automated systems to protect the American public in the age of AI”.
In February 2023, President Biden also signed the Executive Order on Further Advancing Racial Equity and Support for Underserved Communities Through The Federal Government, that “directs federal agencies to root out bias in their design and use of new technologies, including AI, and to protect the public from algorithmic discrimination.”
On October 30, 2023, President Biden signed Executive Order 14110, with the goal of “harnessing AI for good and realizing its myriad benefits” while “mitigating its substantial risks,” This order comprised eight artificial intelligence laws and regulations areas:
- Safety and Security
- Innovation and Competition
- Worker Support
- AI Bias and Civil Rights
- Consumer Protection
- Privacy
- Federal use of AI
- International Leadership.
Now that we have looked into the trajectory of regulation of artificial intelligence along the three prominent administrations, let us study the two most commonly followed AI regulations in the US: the AI Bill of Rights and Executive Order.
The AI Bill of Rights – Things to Take Care of during AI Development
Created by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) to address a demand for stricter US AI regulation, the AI Bill of Rights suggests approaches for making AI transparent, safer to use, and less discriminatory. It also looks into the present and future civil rights-related issues of AI, especially in domains like education, hiring, healthcare, access to financial services, and commercial-grade surveillance.
Here are the principles laid out in this artificial intelligence compliance.
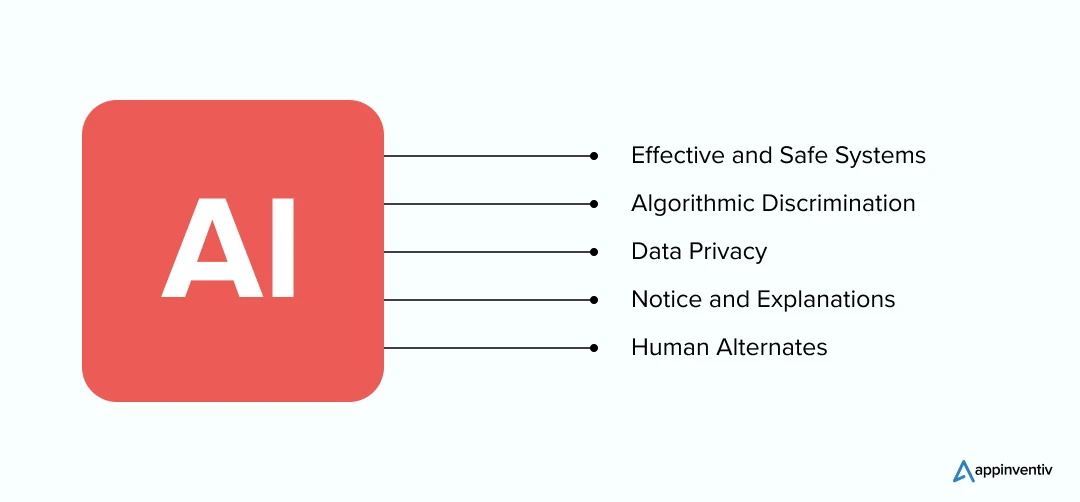
Effective and Safe Systems
The principle states that everybody deserves protection against unsafe and ineffective automated systems. To ensure this, the AI compliance regulation suggests that a diverse set of domain experts and independent parties should be involved in the AI systems development.
These systems must also undergo “pre-deployment testing, risk assessment, and mitigation,” along with continued monitoring, to ensure that they are compliant with all the domain-specific artificial intelligence regulatory compliance standards and that they aren’t used beyond the intended scope.
[Also Read: How to build an AI app? Steps, features, costs, trends]
Algorithmic Discrimination
This happens when specific people are treated unfavorably or unfairly by the automated system because of the biased training data and algorithms.
To safeguard this, the principle suggests that people who are in charge of building and deploying the AI systems should take “proactive and continuous measures” to ensure that the usage of AI compliance in software development is fair and intact.
This would include things like equity assessments, using data that represent multiple groups of ideas and people, ensuring the system can be used by people having special needs, testing and handling biases that come up, and straightforward organization-level oversight.
Data Privacy
This part of the AI regulatory compliance deals with the fact that every individual should have control over the data that they generate digitally and the way it is gathered and used by companies.
As a solution, the policy states that the AI system designers and creators must ask users for their data usage permission most understandably and clearly and then respect their wishes if they refuse to share their data.
Notice and Explanations
This section of the regulation of AI deals with informing people when the AI system is used in a way that can affect them. It implies explaining to people how the system works, the role and scope of automation, and why the system arrived at a certain decision – all of this in a simple, easy-to-understand language.
Additionally, if the system changes the users should be notified before they get invested in the new algorithm or model.
Human Alternates
If a user plans to opt out of an automated system to interact and deal with a human alternative, they should be able to do so whenever it is appropriate.
AI compliance in software development also suggests that individuals must have prompt access to a human if the AI fails, outputs an error, or generates an outcome that the user wishes to explore further or contest.
Ultimately, the AI government regulation states that this process must be made “accessible, equitable, effective, maintained, accompanied by appropriate operator training and should not impose an unreasonable burden” on the users.
While the AI Bill of Rights is only a set of suggestions and is not a legally binding document, it still doesn’t have the weight of law. However, there are some federal protections and guidelines that exist, one of the most prominent of which is the Executive Order on Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence.
The Executive Order – 7 Key Actions to Ensure during AI Development
The Executive Order, as per government regulation of artificial intelligence, mandates the implementation of seven key actions designed to ensure that AI development and deployment are conducted responsibly, ethically, and with consideration for public safety and trust.
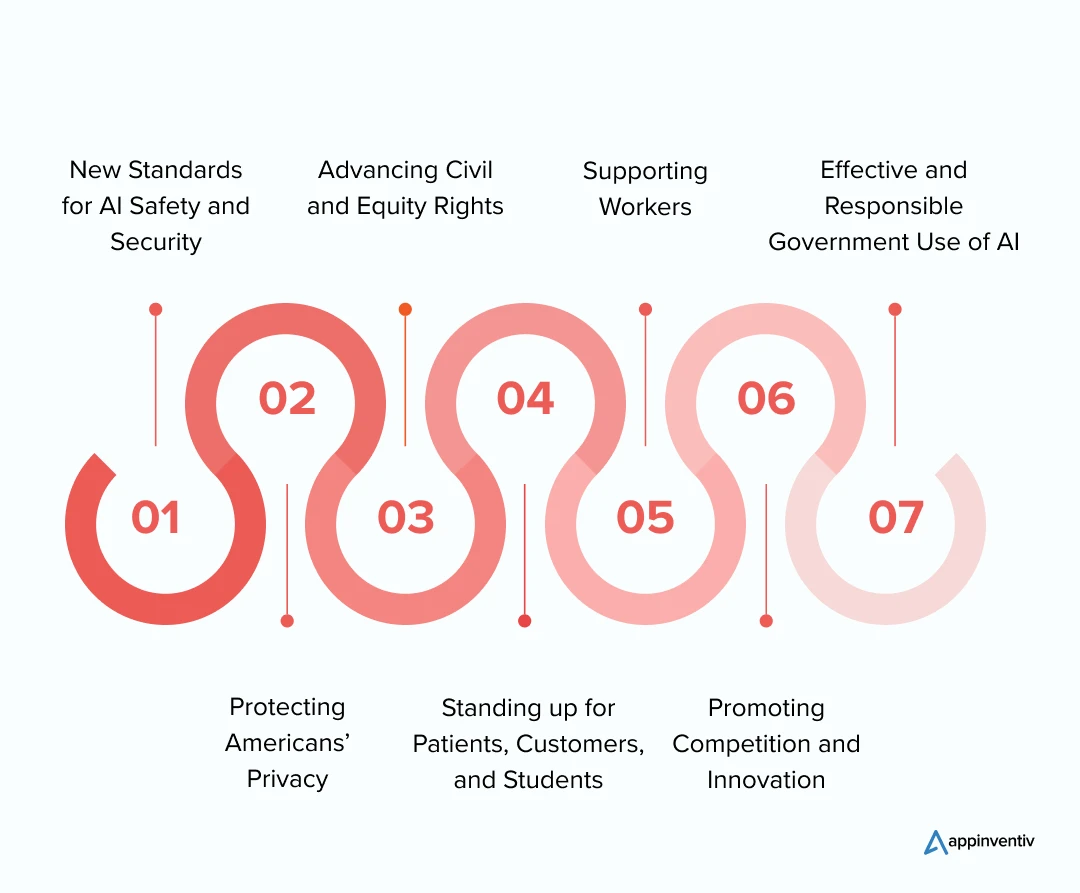
New Standards for AI Safety and Security
With the growing AI capabilities, the implications for Americans’ security and safety are also increasing. The new set of artificial intelligence laws and regulations are aimed at protecting Americans from potential AI risks.
- Developers of powerful AI systems must share the safety results and critical information with the US government.
- Build tools, standards, and tests that ensure the AI systems are secure, safe, and trustworthy.
- Protect against the use of AI in engineering dangerous biological content.
- Protect from AI-led deception and fraud by setting standards and best practices for AI-generated content detection.
- Have a superior-level cybersecurity plan in place for developing AI tools that identify and fix vulnerabilities.
[Also Read: Integrating AI in Cybersecurity – Automating Enterprise with AI-Powered SOC]
Protecting Americans’ Privacy
Without proper regulation of artificial intelligence, Americans’ privacy can be put at immense risk. The technology doesn’t just make extraction, identification, and exploitation of personal data easier but even incentivizes this because the companies tend to use data for developing and training AI models.
- Prioritize federal support for expediting the creation and usage of privacy-safeguarding techniques.
- Strengthen privacy-saving technologies and research.
- Evaluate how the agencies gather and use commercially present data.
- Build guidelines for the federal agencies to measure the effectiveness of privacy-safeguarding techniques.
Advancing Civil and Equity Rights
Irresponsible applications of AI can create and heighten bias, discrimination, and several other abuses in healthcare, justice, and housing. To ensure that there are enough regulations of AI in place to not hinder civil and equity rights, here are the solutions provided by The Executive Order.
- Give clear mentorship to Federal benefits programs, landlords, and federal contractors.
- Solve algorithmic discrimination.
- Maintain fairness in the criminal justice system.
Standing up for Patients, Customers, and Students
AI can offer massive benefits to customers, e.g. making products cheaper, better, and more widely accessible. But artificial intelligence also increases the chance of misleading, injuring, or otherwise harming Americans.
- Build and promote a responsible and explainable use of AI.
- Create an ecosystem that shapes AI’s potential in transforming education.
Supporting Workers
AI is modifying America’s workplaces and jobs, providing both – a promise of better productivity and the challenges of greater bias, workplace surveillance, and job displacement. To address these risks, artificial intelligence laws and regulations state that
- Build practices and principles that eliminate the harm and elevate the benefits of AI for workers.
- Produce a report on AI’s possible labor-market repercussions.
Promoting Competition and Innovation
The Executive Order AI laws and regulations state that America should lead the way in competition and innovation through these actions –
- Perform AI research across the United States.
- Promote an open, fair, and competitive AI ecosystem.
- Use current authorities to expand the capabilities of skilled nonimmigrants and immigrants with the required expertise in critical areas.
Effective and Responsible Government Use of AI
AI can help the American government produce better outcomes. It can even expand agencies’ capability to monitor, govern, and then disburse benefits. Moreover, it can cut down the costs and improve government systems’ security.
- Assist agencies in acquiring specific AI services and products.
- Speed up hiring of AI professionals.
- Issue guidance for the agencies’ usage of AI.
While these are the two US AI regulations that are being suggested or applied on a national level, here is a map view of the state-wise condition of AI in regulatory compliance.
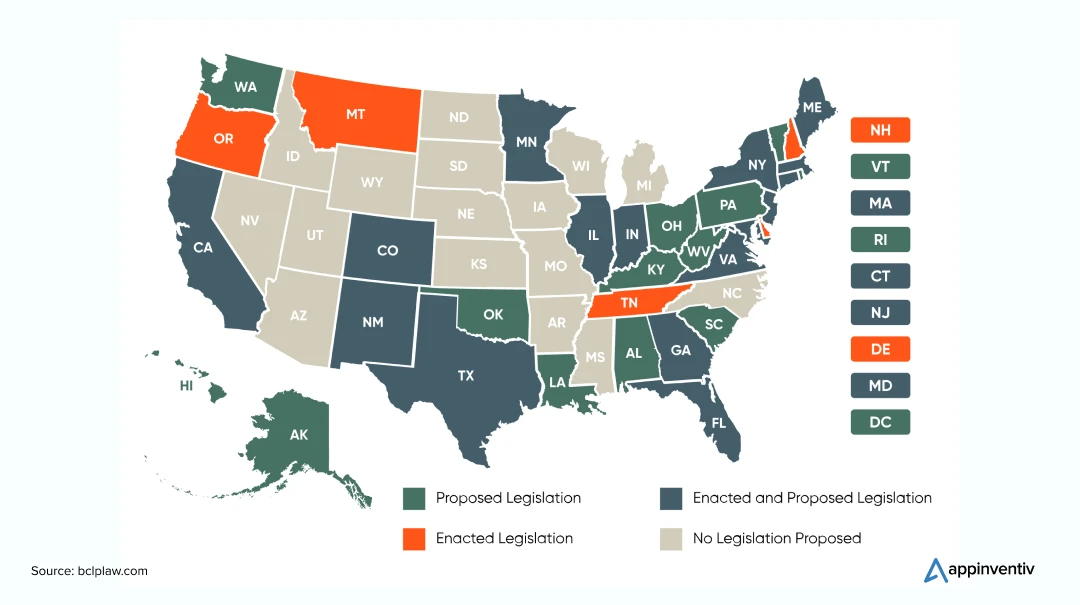
If there’s anything that the current state of AI regulation in the US tells us, it is that there is still time for exact regulations and compliances to come into place. There is a lot for the government bodies to think and plan around considering the ever-growing nature of artificial intelligence technology.
In light of all these artificial intelligence laws and regulations, we understand how confusing it can be for businesses to navigate AI compliance in software development, especially when the technology has found a place in almost every digital use case.
As we conclude the article, let us look into the ways companies can prepare for regulations around AI in risk and compliance along with some examples of industry-wise regulation of AI that should be kept into consideration.
What Businesses Can Do to Prepare for AI Compliance in Software Development?
Having dedicated expertise in AI regulation compliance services and in building a myriad of products using artificial intelligence, the experts at Appinventiv have the technical and market-level know-how of how to prepare you for being compliant.
Although the regulation of artificial intelligence is still developing at a state, federal, and international level, some approaches find common ground in all of these and probably the upcoming sets of US AI regulations.
Know the AI Model
What amount of your operational decisions are made by or are dependent on AI? Do you know which processes are run by AI? Companies should prepare to answer these questions that should be expected to be asked by boards, management, and regulators. In response to this, businesses should map and assess their AI dependencies.
Set the Foundation for AI Adoption
Businesses must build policies that govern how AI technology will be used in their company. The policy must have separate sections, built on constant monitoring, on data integrity, transparency, accuracy, probable risks, and social impacts.
Design Accountability Structures
With AI getting integrated into multiple business processes, businesses should make a dedicated compliance function that would be responsible for setting up and managing AI policies across the entire organization.
Risk assessments
Companies that plan on implementing a new AI model must run a risk assessment and cost-benefit analysis for determining whether the model is even worth implementing. As the risks get identified, companies must establish risk controls (contractual, technical, organizational) and start creating controls in the business units.
According to the Colorado Artificial Intelligence Act (CAIA), there will be strict obligations on developers and deployers of high-risk AI systems to protect consumers from discriminatory decisions. Effective in February 2026, the Act mandates that these entities use reasonable care to prevent “algorithmic discrimination” in areas like education, employment, financial services, and healthcare. It requires annual impact assessments, consumer transparency, and incident reporting of any discriminatory effects.
Communicate
Companies that use AI-based decision-making in their business models should prepare for AI regulation in the US. They should have a strong understanding of their AI system mechanics as they will be asked to give a detailed explanation of the logic their model is based on. We also advise following a strong record-keeping mechanism that would showcase how the system will never create disparate outcomes.
When you prepare to be regulatory compliant, it is important to note that the government regulation of artificial intelligence would vary from one industry to another. For a better explanation, we have picked the top four industries that are considered to be the top choices for AI inclusion.
Financial Services
On March 29, 2021, the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), the National Credit Union Administration, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency together issued a request for information on the financial businesses’ use of artificial intelligence technology. They wanted to help regulators understand the opportunities and challenges of the technology in line with risk management, controls, and governance, along with challenges emerging from the creation, adoption, and handling of AI.
In May 2022, the CFPB issued a circular around compliance in fintech industry that addressed the negative action notice requirements of the Equal Credit Opportunity Act – the one which safeguards discrimination against credit applicants and advised that the conditions “apply equally to all credit decisions, regardless of the technology used to make them,” comprising of AI, and “do not permit creditors to use complex algorithms when doing so means they cannot provide the specific and accurate reasons for adverse actions [such as declined applications].”
In June 2022, the American Data Privacy Protection Act (ADPPA) – the first bicameral, bipartisan federal privacy bill – was presented in Congress. If passed, AI compliance in the banking industry and their fintech counterparts would need them to provide for better transparency in the system, utilization, and selling of consumer data; provide lesser safeguards for data security; and call for management supervision of data security and privacy.
Automotive
The inclusion of AI in the automotive industry can be seen primarily in automated driving systems.
While there have been instances where the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) issued a Standing General Order requiring operators and manufacturers and operators of automated driving systems to report crashes to the agency, on a national stage, AI regulatory compliance in automotive industry has not been able to keep up with the speed of AVs development.
NHTSA, however, is planning to build a framework that would ensure automated driving systems are deployed securely.
Healthcare
In the 2021 action plan, the FDA highlighted five goals for the management of AI/ML-powered Software as a medical device (SaMD).
- A tailored regulatory framework that would outline the ‘what’ of an AI system can be built through learning and how the system would implement adaptation while being effective and safe.
- The next part of the regulation of AI in healthcare highlights ten principles that can promote effective, safe, and high-quality devices.
- Patient-focused approach should be brought into practice that can ask an AI system why it made certain recommendations.
- Reduce algorithm bias by using a range of data sets led by ethnicity, race, and socioeconomic status.
- Real-world performance insights should be provided to give manufacturers an insight into product usage, areas of enhancements, and help them fix user-friendliness challenges.
AB 311, presently under consideration by the California Assembly, applies to both healthcare and other sectors, requiring them to –
- Submit yearly impact assessments
- Communicate the reason behind AI’s decisions
- Allow the users the opportunity to interact with a human
- Build safeguards, document the solution’s limitations, and share them with the users of the model.
- Establish a dedicated compliance team.
Insurance
In July 2023, the Securities and Exchange Commission suggested some rules as a part of their regulatory compliance in insurance industry “that would require broker-dealers and investment advisers (“Firm”) to take certain measures to address conflicts of interest associated with their use of predictive data analytics and similar technologies to interact with investors to prevent firms from placing their interest ahead of investors’ interests.” The suggested policy would apply when the insurance firms would use of can be expected to use AI technology in an investor interaction.
We understand how intimidating AI compliance regulations can get, especially when the laws are still at a development stage and vary from one state and industry to another. While we hope that this extensive article helps you get some insights into the top two federal-level AI regulations in the US, we also commit to translating this set of regulations into a compliance-ready AI product through our advanced-grade artificial intelligence development services.
According to a report by Wall Street Journal, more than 27% of the Fortune 500 businesses are now worried about the AI regulations and laws concerning their operations and are bracing for challenges related to legal liabilities, compliance costs as well as disruption to innovation. Thus, as AI legislation gains momentum across the US and globally, it’s high time for businesses to partner with AI development firms like Appinventiv that are well-versed with the ins and outs of the evolving AI landscape and can help them prepare for stricter oversight.
Get in touch with our technology and compliance experts today to get on a path where you build a compliant application.
FAQs
Q. What is the importance of AI compliance?
A. AI compliance is critical for multiple reasons. It can help with ensuring an ethical and responsible use of AI, protect user privacy, prevent AI biases, and fosters trust in the artificially intelligent systems.
Compliance with regulations can also help eliminate legal risks, promote fair and transparent AI practices, and encourage the development of AI solutions that benefit society on a holistic level.
Q. How to ensure AI compliance in software development?
A. In order to ensure AI compliance in software development, it’s crucial for businesses to adhere to relevant data protection and privacy regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, etc. In addition to this, regular audits and updates should be conducted to align with the legal standards. Businesses should also incorporate ethical AI practices and transparent documentation throughout the AI development process in order to maintain accountability as well as trust.
Q. How to regulate AI?
A. Regulating AI will call for a multifaceted approach where all the legal, ethical, and technical aspects are covered. While the agenda behind AI regulation is straightforward – protecting users from biased, false, and harmful information, a collaboration between governments, industry, academia, and the public will be needed to approach this.
Q. Why does every business need to pay attention to AI compliance?
A. There are a number of reasons why every business should care about being AI-compliant.
Every business should pay attention to AI compliance for several important reasons:
- Ethical and reputation concerns
- Fairness and avoiding bias
- Privacy protection
- Risk management
- Global standards and market access
- Avoiding regulatory penalties
- Staying competitive
- Long-term viability
Q. How should the government approach AI and regulatory compliance?
The introduction and development of AI-based solutions are growing massively across the US and even globally. In the span of the next 10-20 years, almost every government agency and business will be using AI. This, in turn, will have a deep impact on the economy, society, and even national security. Noting this, here’s what we think should be at the core of regulations around AI in risk and compliance.
Efficiency: Policymakers should measure the applicability of current AI compliance regulations. Only the accurate enforcement of current regulations and laws will offer regulatory assurance and guidance to the stakeholders and help them assist the policymakers in building future regulations and laws.
Neutrality: AI regulation in the US must be completely technology-neutral and should concentrate on the outcome and applications of AI, instead of the technology itself. Laws around AI must be built solely as a necessity to fill the gaps in the current laws, protect citizens’ rights, and foster public trust.
Proportionality: As soon as policymakers find gaps in the AI laws and regulations, they must adopt a risk-inclined approach toward AI regulation. This strategy would make sure that there is a proportionate and balanced approach to creating a well-strategized AI government regulation.
Collegiality: AI applications are complex, cross-cutting, and constantly changing and will need a coordinated, strategic approach that involves multiple agencies. This would ultimately allow agency and sector experts to have the capability of narrowing in on the most critical emerging challenges in their specific areas.
Flexibility: AI and regulatory compliance must encourage the private sector to approach innovation and risk assessment. The policymakers must promote approaches that are built collaboratively with technical experts, government, civil society, and the private sector. This would help the laws be agile in terms of keeping up with the constantly changing AI technology landscape.



How Much Does It Cost to Build an AI Trading App Like Moomoo?
Trading apps have undoubtedly solved the major pain point of the public - eliminating middlemen from investing their money, Which keeps them in fear that they might get cheated or lose their money. However, trading apps have facilitated users with the transparency to perform trading safely and swiftly. In the era of smartphones and AI,…
15 Explorative Use Cases of AI in Mortgage Lending
In an era where technological advancements are revolutionizing every sector, mortgage lending has been slow to embrace change. The industry has been bogged down by outdated processes, increasing operational costs, and regulatory pressures. However, with the introduction of AI in mortgage lending industry, a shift is occurring that promises to address these pain points while…

How to Develop AI Medical Transcription Software? Costs, Process, and Benefits
Developing accurate and efficient medical transcriptions manually has always been a painstaking process, fraught with many challenges. Manual transcription often leads to errors, misinterpretations, delayed patient care, and the high costs associated with hiring skilled professionals. As the volume of medical data grows, the pressure to maintain accuracy without compromising efficiency intensifies. It's time to…







